An Experimental Study on The Failure-Tolerant Control of a Redundant Planar Serial Manipulator Via Pseudo-Inverse Approach
Abstract
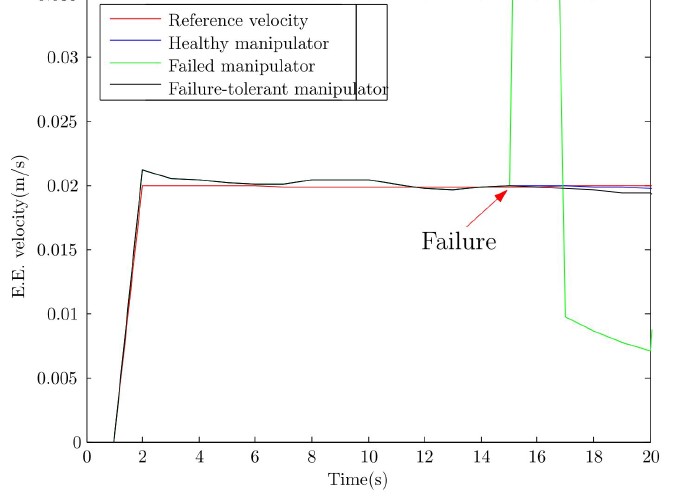
In this paper, fault-tolerant control of redundant planar serial manipulators has been investigated experimentally via an offline method called psuedo-inverse reconfiguration method. Minimizing the end-effector’s velocity jump via an optimal mapping of joint failures into healthy joints velocity space can be regarded as the main contribution of this reconfiguration approach. This algorithm has been simulated and implemented on a four-link serial manipulator named as TaArm. It should be mentioned that for simulation and practical tests, C++ programming language in QtCreator environment has been used which provided high computational speed. Two scenarios has been selected for simulation and implementation studies and results shows that the algorithm considerably removes the velocity jump of the end-effector in both simulation and experimetal studies.